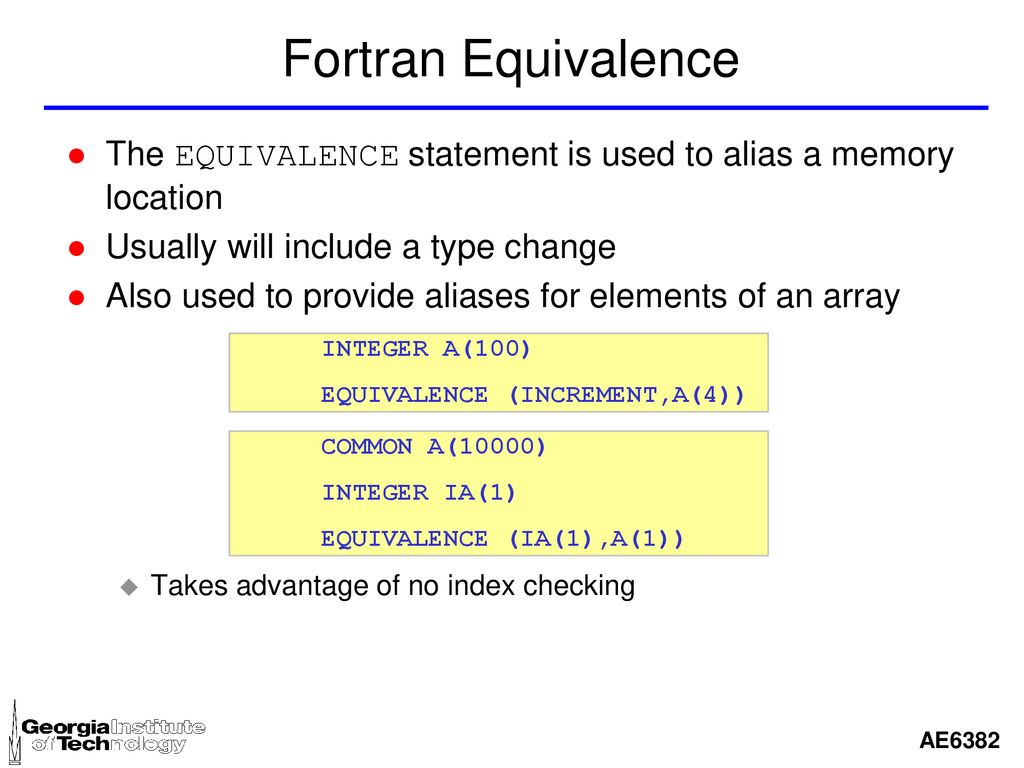
FORTRAN TYPE CONVERSION Peter Smart home computing index Conversion to and from Character Conversion to Integer Conversion to Nearest Integer Conversion to Real Conversion to Nearest Real Truncation of Real Conversion to DoubleAn extensible derived type may be abstract type, abstract base_type end type Such a derived type may never be instantiated, such as by type (base_type) t1 allocate (type (base_type) t2) but a polymorphic object may have this as its declared type class (base_type), allocatable t1 or function f (t1) class (base_type) t1 end functionType FUNCTION functionname (arg1, arg2, , argn) IMPLICIT NONE specification part execution part subprogram part END FUNCTION functionname ztypeis a Fortran 90 type (is a Fortran 90 type (egeg, INTEGERINTEGER, REAL, LOGICAL, etc) with or without KIND zfunctionname isaFortran90identifieris a Fortran 90 identifier

1 1 Lecture 1 Introduction To Fortran Program And Numerical
Fortran type
Fortran type-Programming in Modern Fortran Namelists Namelists are an I/O feature for formatfree input and output of variables by keyvalue assignments that were first introduced by some FORTRAN 77 compilers, but then became a Fortran 90 standard laterSynopsis MPI_Sizeof(v,size) Returns the size, in bytes, of the given type Fortran MPI_SIZEOF(V, SIZE, IERROR) V INTEGER SIZE, IERROR Input parameter V A Fortran variable of numeric intrinsic type (choice) Output parameter size Size of machine representation of that type (integer) ierror (Fortran) Error status (integer);




Bab 4 Listing Program Fortran
Defining your own types in F90 A user defined type is defined in Fortran 90 as follows TYPE TypeName type1 ,attr A user defined type is defined in Fortran 90 as follows TYPE TypeName type1 ,attr element1;Modern Fortran Fixing the Flaws Structures and Derived Types • Declaration specifies a list of items (Derived Type) • A Structure (a variable of a derived type) can hold – variables of simple type (real, integer, character, logical, complex) – arrays static and allocatable – other derived types – A structure can be allocatableLanguage and the FORTRAN IV translator or compiler The FORTRAN IV language is composed of mathematical form statements constructed in accordance with precisely formulated rules FORTRAN IV programs consist of meaningful sequences of FORTRAN statements intended to direct the computer to perform the specified operations and computations
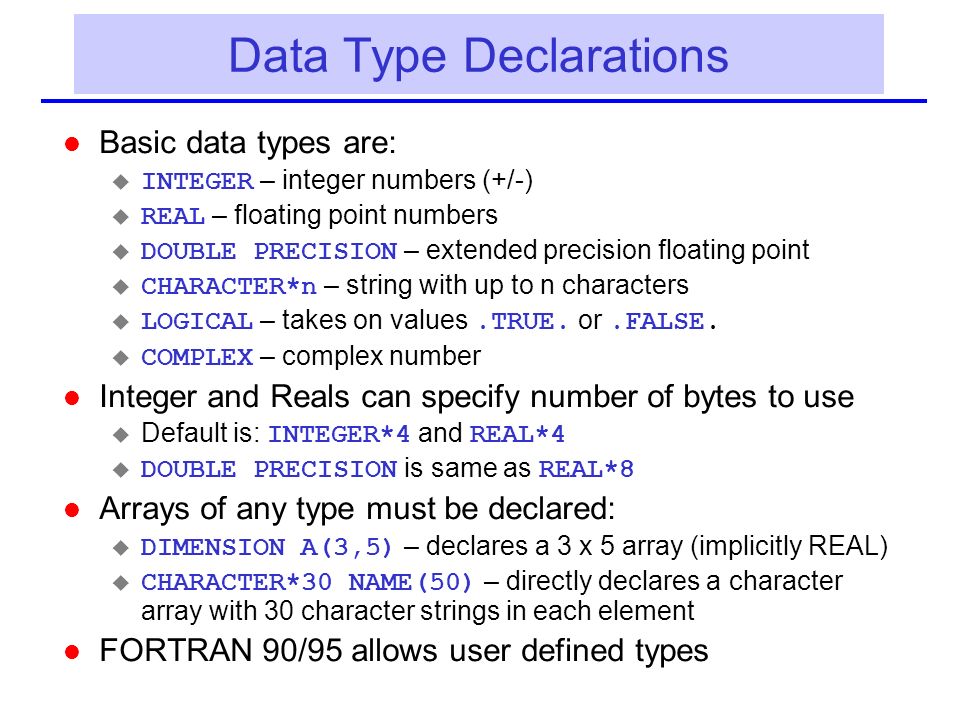
Complex numbers are common in many fields of science and engineering so it is not surprising that FORTRAN 77 offers a COMPLEX data type The complex number aib where i is the imaginary unit (square root of 1) is represented in FORTRAN 77 as (a,b) where a and b themselves are single precision REAL numbers To read data written in a compound type, you must know its structure Use the NF90_INQ_COMPOUND functions to learn about the compound type In Fortran a character buffer must be used for the compound data The user must read the data from within that buffer in the same way that the C compiler which compiled netCDF would store the structureFortran has five intrinsic data types INTEGER, REAL, COMPLEX, LOGICAL and CHARACTER Each of those types can be additionally characterized by a kind Kind, basically, defines internal representation of the type for the three numeric types, it defines the precision and range, and for the other two, the specifics of storage representation
Deferred procedures are those functions/subroutines that will be implemented in a specific derived type To illustrate it, our problem requires a generic class that enforces == property This can be usefull when using unlimited polymorphic types class(*) Fortran classes must implement/overload the generic '==' so it is possible to compare themDatatype called LOGICAL This was a Boolean datatype withtwo states true or false At the end of the seventies Fortran 77 was introduced This version contained better loop and test structures In 1992 Fortran 90 was formally introduced as an ANSI/ISO standard This version of Fortran has made the language into a modern programming languageA Fortran derived type is interoperable with C if it has the BIND attribute This release of the Fortran 95 compiler implements these features as described in the chapter 15 of the draft standard Fortran also provides facilities for defining derived types, enumerations, and type aliases that correspond to C types, as described in chapter 4 of the draft standard



Message Data



Bindto User Guide Cbfortran
Fortran 77 has only one type for integer variables Integers are usually stored as 32 bits (4 bytes) variables Therefore, all integer variables should take on values in the range m,m where m is approximately 2*10^9 Fortran 77 has two different types for floating point variables, called real and double precisionThe INTEGER (KIND=2) and LOGICAL (KIND=2) types are not necessarily supported by every GNU Fortran implementation This corresponds to types that occupy as much storage as the default CHARACTER type, which is the same effective type as CHARACTER (KIND=1) (making that type effectively the same as CHARACTER (KIND=3) )The format string * will cause Fortran will use "default" printing (each type of variable will have its own default format) Example PRINT *, Variables WRITE (6, *) Variables Taylormade Format Strings The format string in a print or write controls the manner printing the values The syntax of a




Midterm Review Programming In Fortran Yi Lin Feb




5 Real Data Type Supported By The Fortran Compiler Download Table
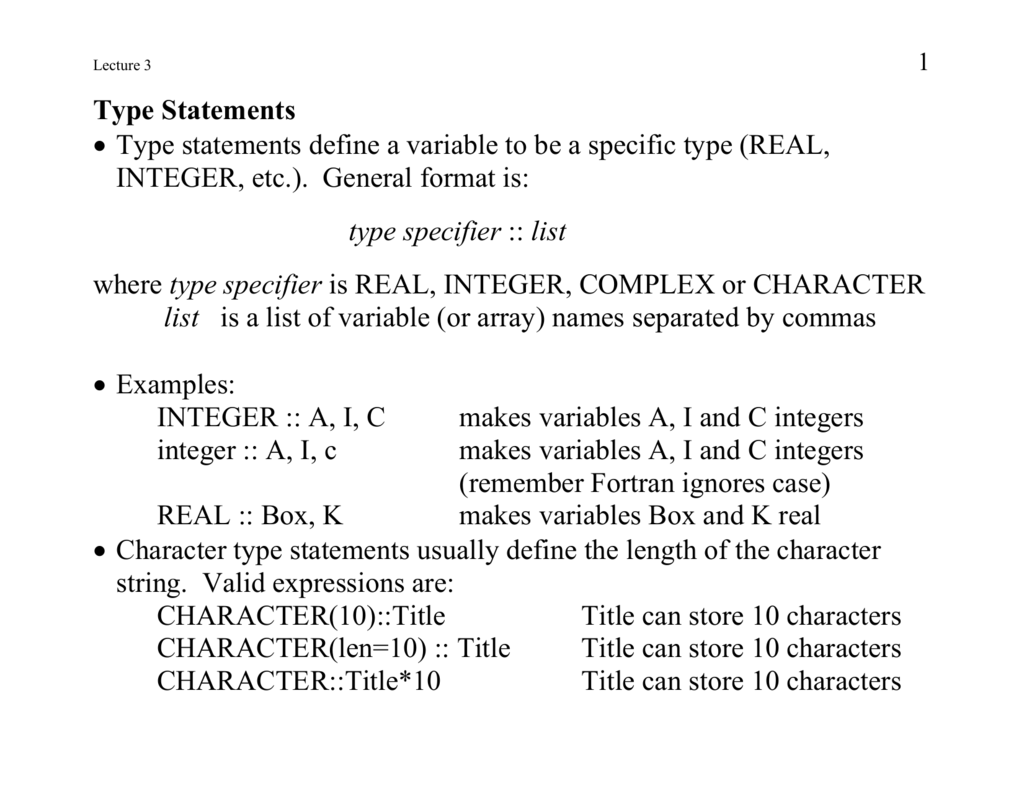
ZThere are four types of operators in Fortran 90There are four types of operators in Fortran 90 arithmetic, relational, logical and character zThefollowingshowsthefirstthreetypesThe following shows the first three types Type Operator Associativity Arithmetic ** right to left * / left to right lefttorightleft to rightType2 ,attr After defining the typeFor each data type and corresponding constant there are what are called declaration statements, which are used to define the type of data to be associated with a chosen FORTRAN variable Thus INTEGER K, PTR REAL SUM, COST, VALUE CHARACTER (LEN=) NAME, ADDRSS LOGICAL SINGLE




A Browser Based Tool For Conversion Between Fortran Namelist And Xml Html Sciencedirect




Fortran Derived Data Types
Fortran issue Argument of "xx" is one type at (2) but is some other type at (1) 4 Fortran Initialize character string with unknown length in main program 2 What is actually "typebound subroutine" in Fortran and related?Fortran, as derived from Formula Translating System, is a generalpurpose, imperative programming language It is used for numeric and scientific computing Fortran was originally developed by IBM in the 1950s for scientific and engineering applications Fortran Array Data and Arguments, Vectorization Examples The modern Fortran language has various types of arrays and an array sectioning feature that enables subsections of arrays to be passed as parameters to functions or be pointed by Fortran pointers For loops that operate on arrays, the compiler can generate unit stride vector code, non




Fortran Programming Language Getting Started With The Fortran



Creating The Fortran Com Server Windows
The Fortran 90 Handbook is a definitive and comprehensive guide to Fortran 90 and its use Fortran 90, the latest standard version of Fortran, has many excellent new features that will assist the programmer in writing efficient, portable, and maintainable programs TheFortran 90Fortran 90 has the generic conversion functions INT (x,kind), REAL (x,kind) with the kind arguments being optional If kind is ommitted, conversion is done to default kind Arguments x may be of any numerical type and kind and may be scalars or arrays Latter ones areFortran 77 has only one type for integer variables Integers are usually stored as 32 bits (4 bytes) variables Therefore, all integer variables should take on values in the range m,m where m is approximately 2*10^9 Fortran 77 has two different types for floating point variables, called real and double precision




Example Of Fortran Code And Device Variable Point Wise Expression Download Scientific Diagram




Fortran 95 Code Defining Type Quad Download Table
Fortran 90 Derived Data Types The Fortran 90 derived data type is similar to C structures and also has some similarities with C classes The syntax for declaring a derived type, is An array of mytype can also be createdA derived type is extensible if it has neither the bind attribute nor the sequence attribute Such a type may be extended by another type A polymorphic variable with declared type base_type is type compatible with type higher_type and may have that as dynamic type Type compatability descends through a chain of children, but a type may extendThe fftw_iodim64 type in the 64bit guru interface (see 64bit Guru Interface) is the same, except that its components are of type integer(C_INTPTR_T) Using the wisdom import/export functions from Fortran is a bit tricky, and is discussed in Accessing the wisdom API from Fortran



우림텍 Lf Gnu Fortran




Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink
Fortran 90/95 Programming Manual Real Type For real numbers (such as 314, , 10 etc) A processor must provide two different real types The default real type and a type of higher precision, with the name double precision Also this is a legacy of FORTRAN 77 FortranLikewise, if you insert the statement A = sqrt (5), Fortran will truncate sqrt (5) = and deduce that A = 2 But errors such as these are easily avoided if you are careful to make correct type declaration statements for all variables at the beginning ofWith Fortran 90, you can define your own generic procedures so that a single procedure name may be used within a program, and the action taken when this name is used is dependent on the type of its arguments This is also known as polymorphic typing




Fortran The History Of Fortran N Before Fortran




Fortran
Fortran Data Types Integer Type The integer types can hold only integer values Note that the huge () function gives the largest Real Type It stores the floating point numbers, such as , , , etc Traditionally there are two Complex Type This is used for storingFortran 90 has no concept of unsigned integers, nor 1 byte or 2 byte integers It has a single, signed integer type, typically of 4 or 8 bytes (Fortran 03 adds new types for C interoperability) Arrays Arrays can have up to 7 dimensions, specified within ( ) parenthesis Status In Fortran 77, double precision was one of the six intrinsic data types, but since Fortran 90 it has been relegated to being an alias for the higher precision kind of the real type Action None required, but ideally new code should make use of the SELECTED_REAL_KIND function to select the kind of a floating point variable according to



Getting Started With Fortran




How To Write A Matrix In Fortran 90
3 NetCDF Startcount exceeds dimension bound 2C pointers are represented in Fortran via the special opaque derived type type (c_ptr) (with private components) Thus one needs to use intrinsic conversionAs discussed previously in Variables, there are five builtin data types in Fortran A derived type is a special form of data type that can encapsulate other builtin types as well as other derived types It could be considered equivalent to struct in the C and C programming languages




Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Docsity



Ptp Photran Documentation Photran5 Eclipsepedia
Fortran 77 Data Type Size Default Alignment SPARC x86 Alignment in COMMON SPARC x86 BYTE X CHARACTER X CHARACTER*n X 1 1 n 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 COMPLEX X COMPLEX*8 X DOUBLE COMPLEX X COMPLEX*16 X COMPLEX*32 X 8 8 16 16 32 4 4 8 8 8/16 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 DOUBLE PRECISION X REAL X Again, you don't have to pass the type, since the compiler can figure it you from the variable itself But it has to be a polymorphic type Both Intel ifort and gfortran list select type and polymorphic datatypes as supported the later with some experimental aspects in gfortran (http//gccgnuorg/wiki/Fortran03) These are recent additions to these compilers This question was motivated by one in the math SE in which someone commented that he preferred to reserve i, j, k for integers Of course, another common use for i in maths is sqrt(1) Which reminds me that Fortran is the only language that I know with a builtin complex type




8 0 Type Declaration In Fortran Implicit Explicit Youtube



1




Lecture 14 Transition From Fortran To C Ii




Chapter 2 Basic Elements Of Fortran 2 4
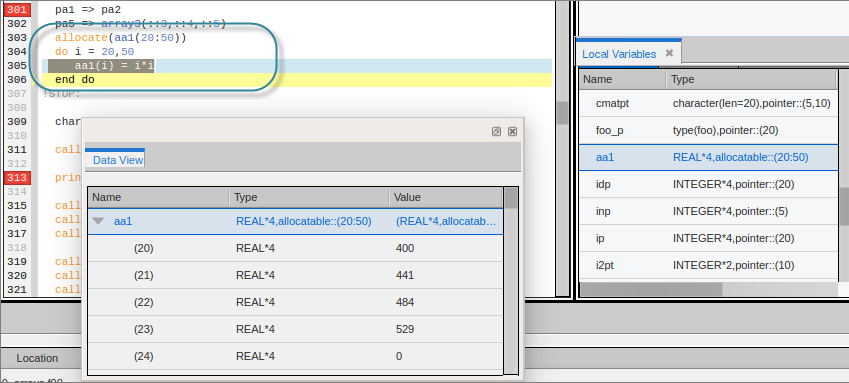



Fortran 90 Deferred Shape Array Types
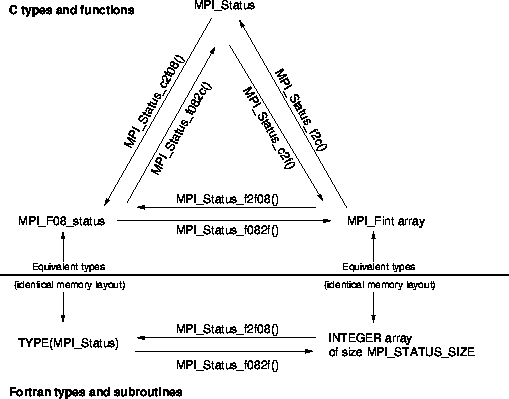



Status




Fortran 95 And Fortran 03 Tips And Techniques
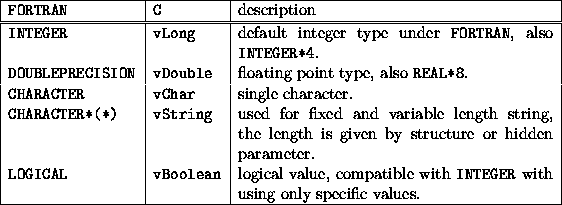



Fortran C Binding




Modern Fortran Explained Incorporating Fortran 18 By Metcalf Michael Reid John Cohen Malcolm Amazon Ae



Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 003 Implicit None Simple Data Types Youtube
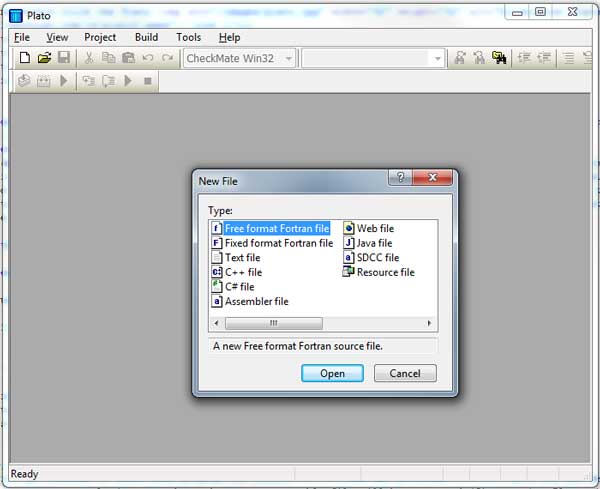



Fortran Tutorial Free Guide To Programming Fortran 90 95 Introduction




Github Stanislavradkov Fortran Cheat Sheet Fortran Cheat Sheet




Fortran Loops




Chapter 4 Data Types



In What Type Of Work Is The Fortran Programming Language Most Used Today Quora




Mk Dynamics Programming Programming In Fortran



Absoft Pro Fortran



Introduction To Fortran Ppt Video Online Download




Modernizing Modularizing Fortran Codes With 03 Standards




Chapter 11 More Fortran Elements Functions And Subroutines 11 1



Fortran 90 Pointer Type



Fortran 90 Pointer Types Totalview User Guide V6 3
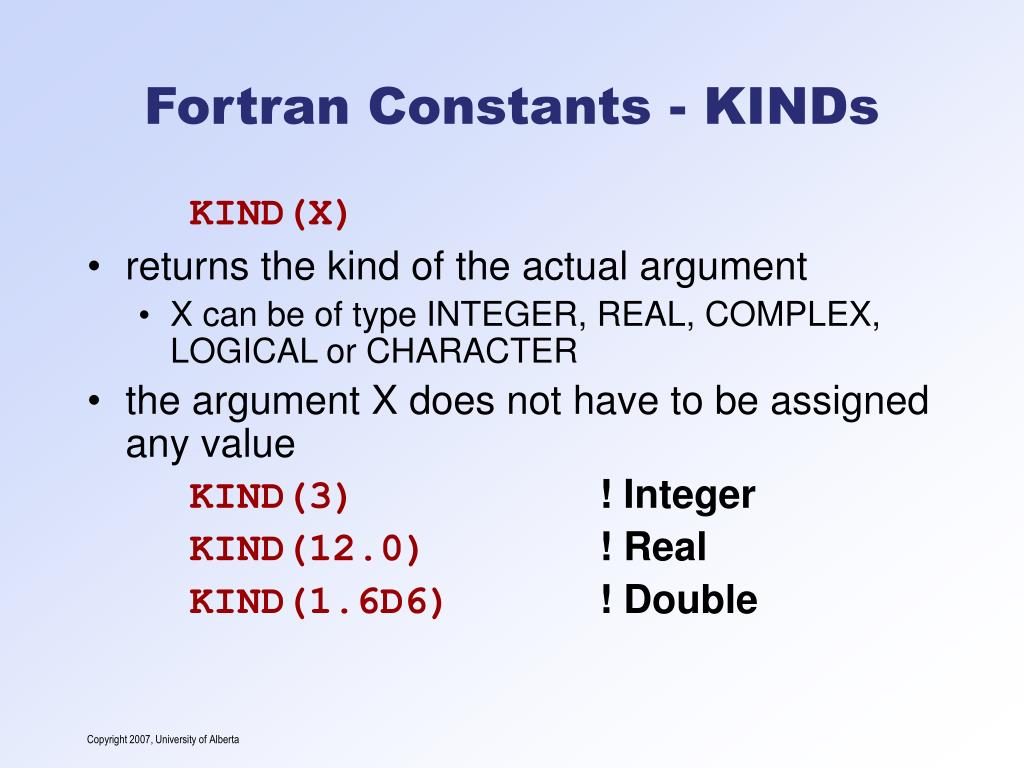



Ppt Introduction To Fortran Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




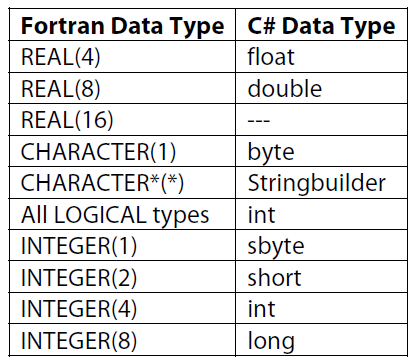
Cross Referencing Between Basic Data Types In Fortran And C Th Th Download Table




Fortran Wikipedia




History Of Computing Fortran Ppt Download




Fortran




1 1 Lecture 1 Introduction To Fortran Program And Numerical




Fortran Matthew Cars On History Of Fortran Fortran



File Type Fortran Free Icon Of Vscode




The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience




Fortran 90




Fortran Basics Pdf Pointer Computer Programming Parameter Computer Programming



Ppt Fortran 90 95 And 00 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Uobabylon Edu Iq




Confluence Mobile Ecmwf Confluence Wiki
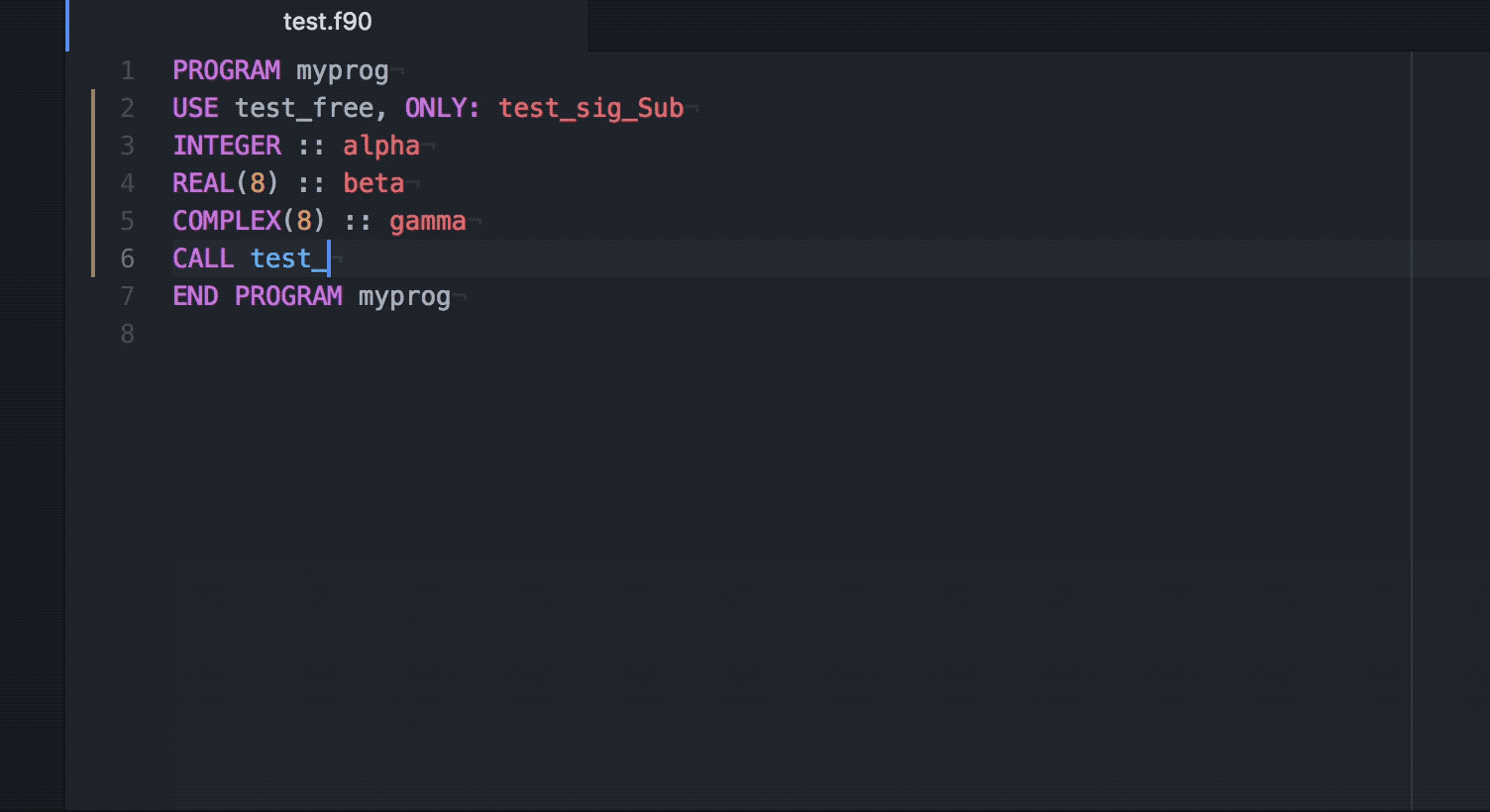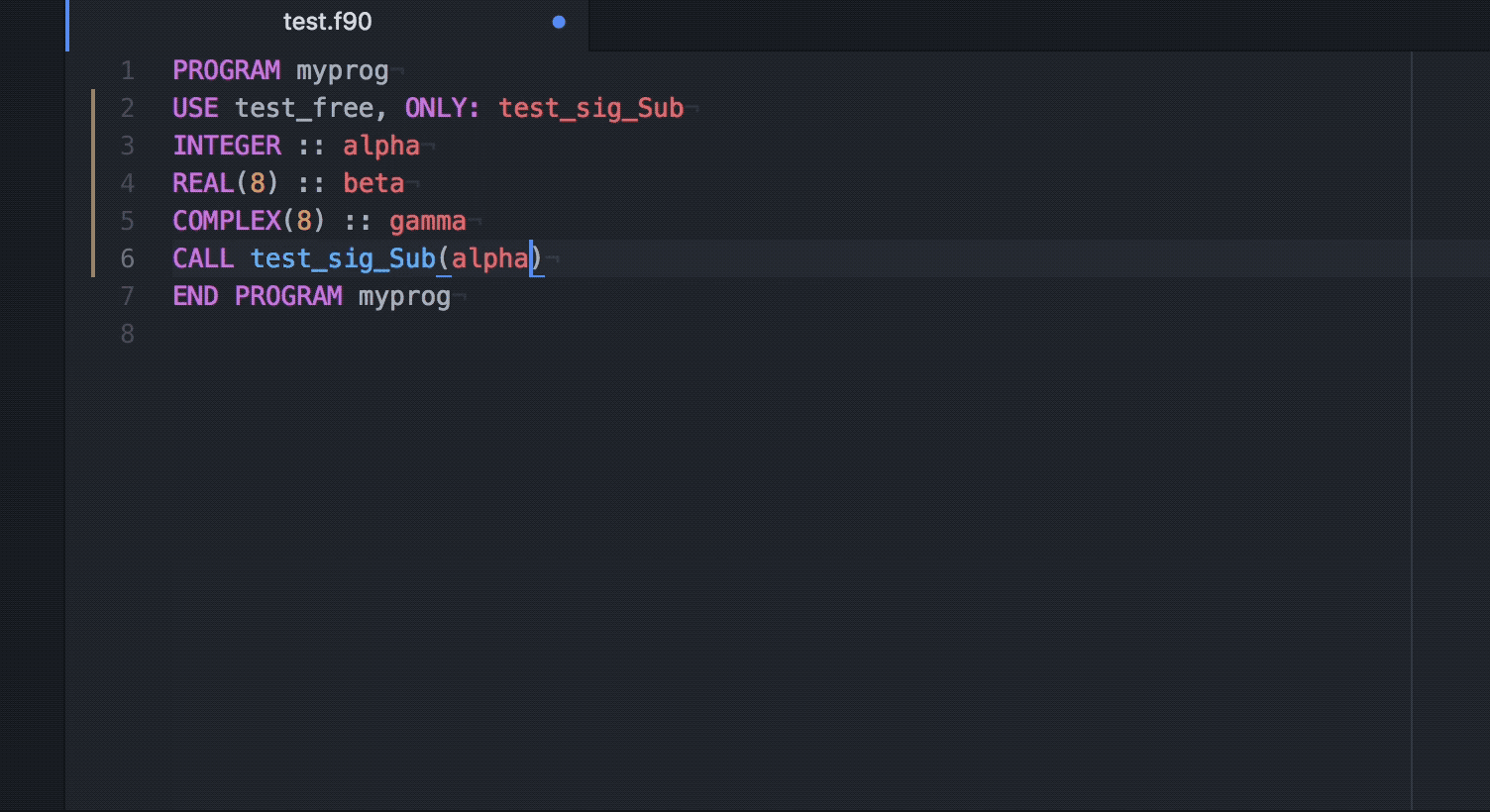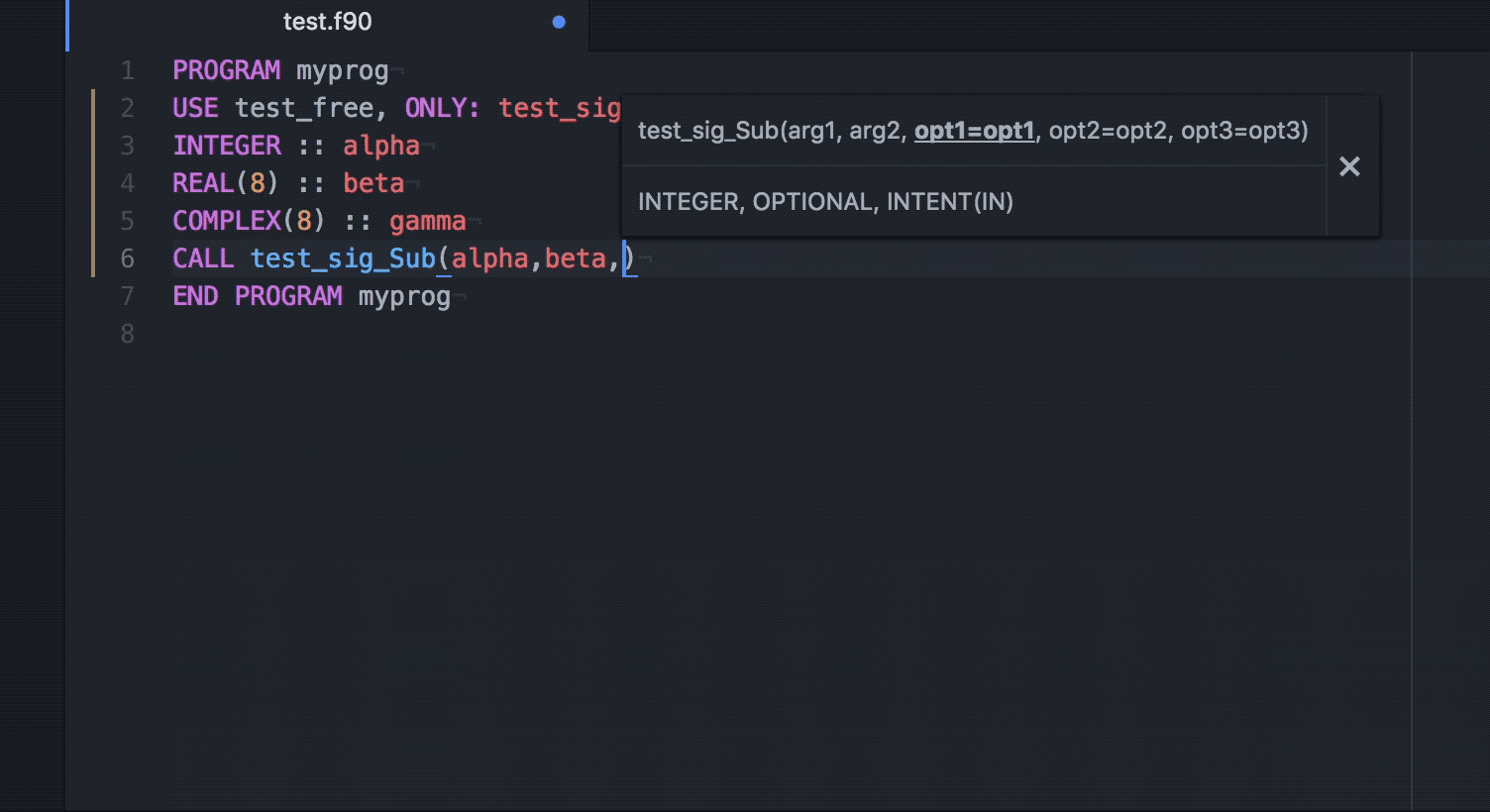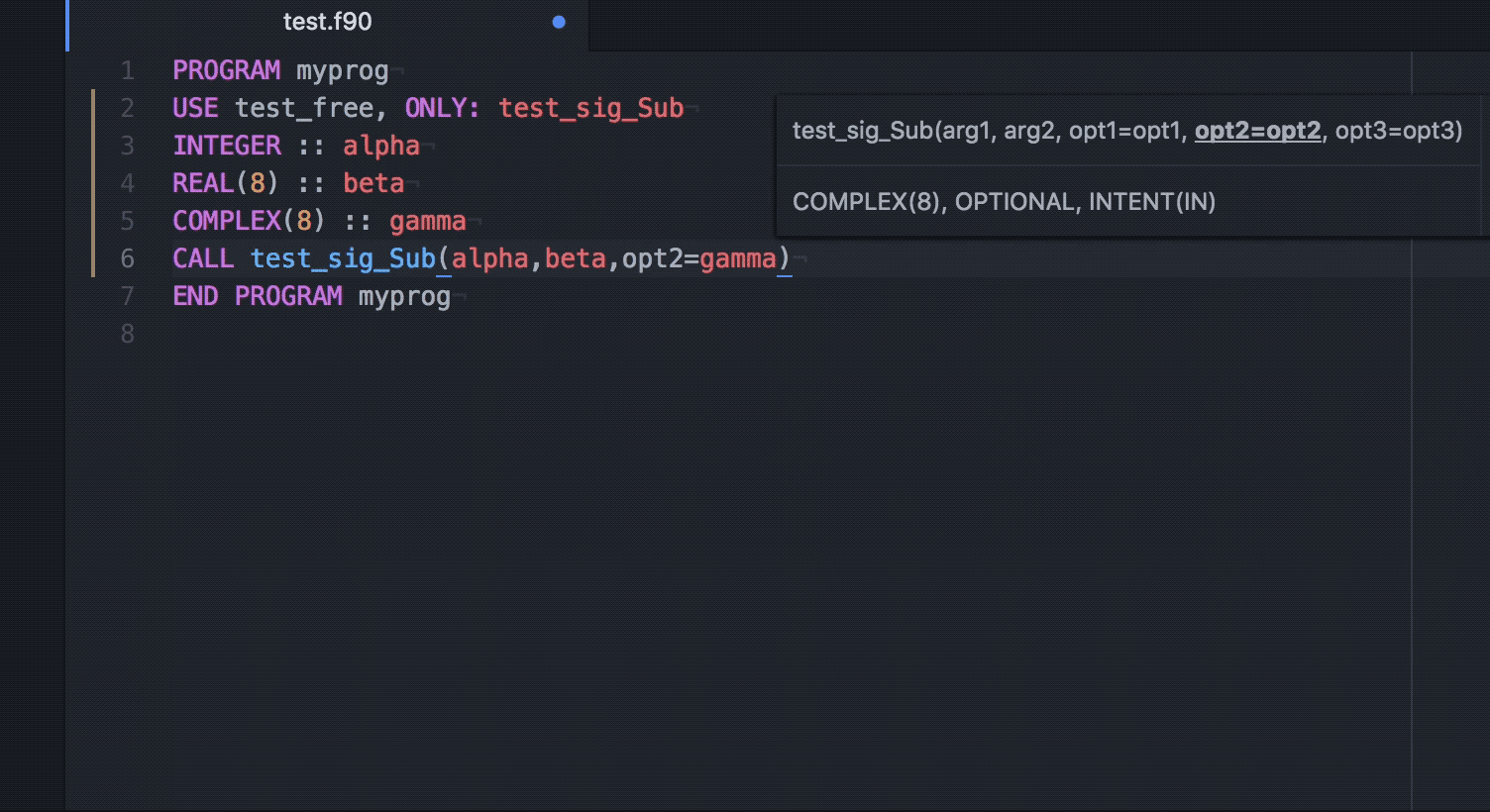



Ide Fortran



History Of Computing Fortran Ppt Download




Fortran Arithmetic Error Stack Overflow



Simply Fortran From Approximatrix




Fortran 90




Bab 4 Listing Program Fortran



Type Mpi Character




Essence Of Fortran Multi Dimensional Array Emulation In C We Note Download Scientific Diagram




How To Program In Fortran With Pictures Wikihow




Advanced Fortran Programming 021 Derived Data Types Youtube



Cds Cern Ch



Making Legacy Fortran Code Type Safe Through Automated Program Transformation Springerlink




Data Types In Fortran Code Blocks Tutorial 3 Real Integer Double Complex Logical Character Youtube



Getting Started With Fortran



1




Chapter 4 Data Types



Tutorial Starting A New Object Oriented Fortran Project In Code Blocks The Delocalized Physicist




Fortran 90 User Defined Types




Intel Fortran Compiler Ifort Fasrcc




Elementary Fortran Elementary Fortran 77 Z All Fortran



1




How To Program In Fortran With Pictures Wikihow



Accessing Fortran Legacy Dll In C Code Masala Ranjeet Sharma



Lahey Fortran Professional V7 6 Windows
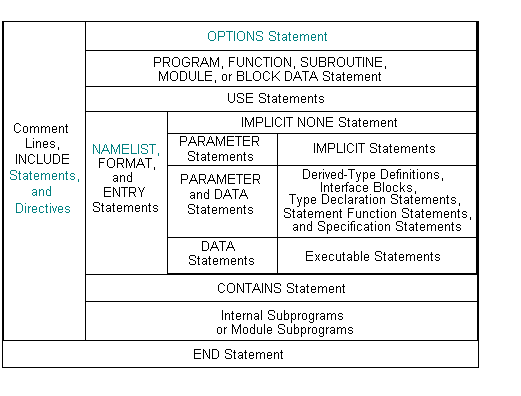



Statements




Fortran 95 Code Defining Type Quad Download Table




Fortran 90 Notes Pdf Document



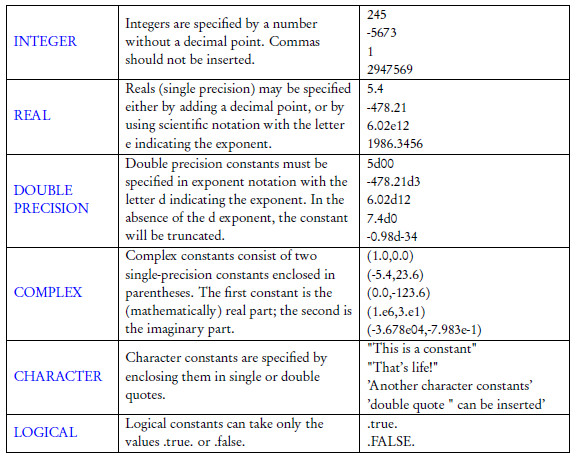
Constants Variables And Arrays




Modern Fortran Explained Numerical Mathematics And Scientific Computation Metcalf Michael Reid John Cohen Malcolm Amazon Com Books



Send Buffer And Message Data




Shows A Fortran 90 Program That Defines A New Type Called Node The Download Scientific Diagram




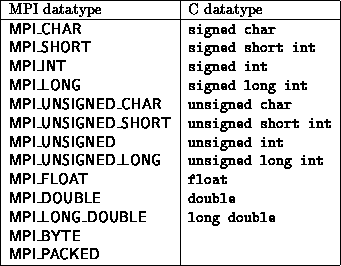
Basic Fortran Datatypes In Mpi Mpi Datatype Fortran Datatype Download Table




Unclassifiable Statement In Fortran Using Matrix Stack Overflow
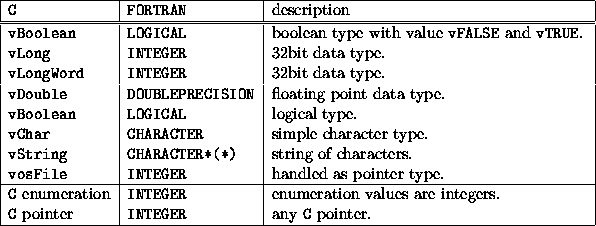



C Fortran Binding



Fortran 90 User Defined Types Totalview User Guide V6 3




Fortran Specification Statements Session Six Icocsis Ppt Download
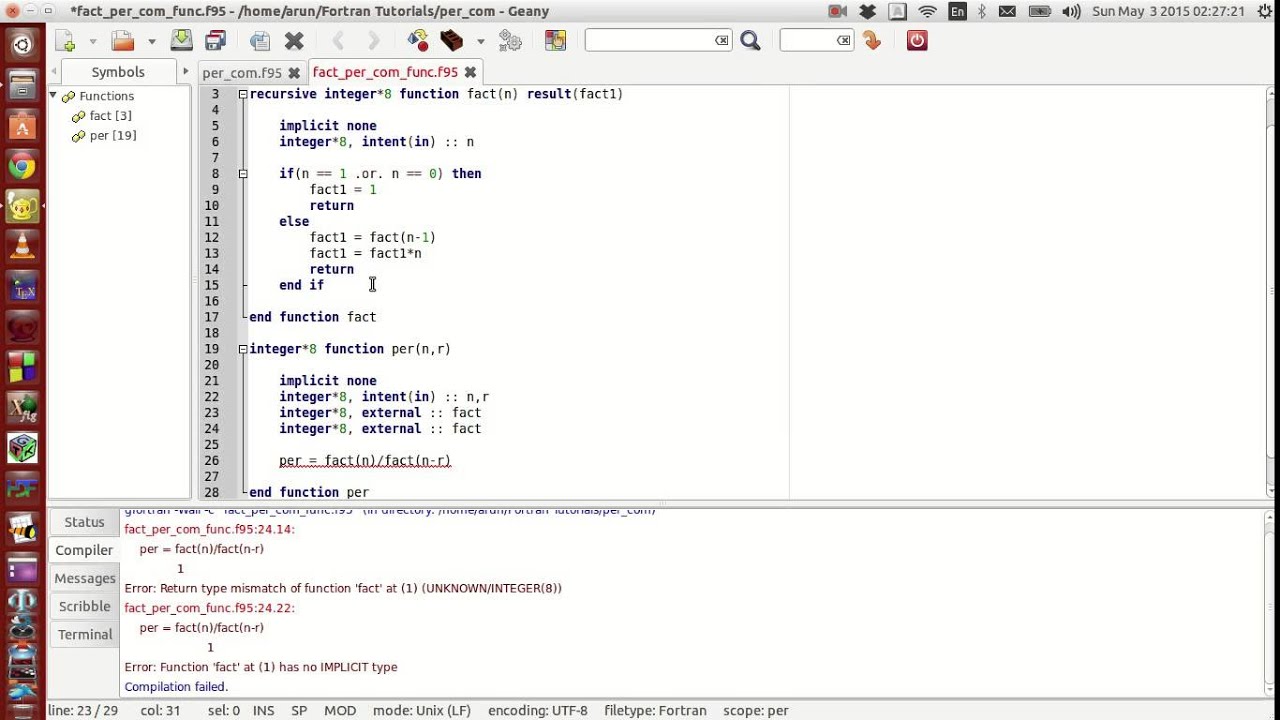



Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 033 Recursive And Multi Function Calls Youtube




Fortran 90 Write Format




Fortran Wikipedia




Fortran 90




Fortran Tutorial




8 0 Type Declaration In Fortran Implicit Explicit Youtube
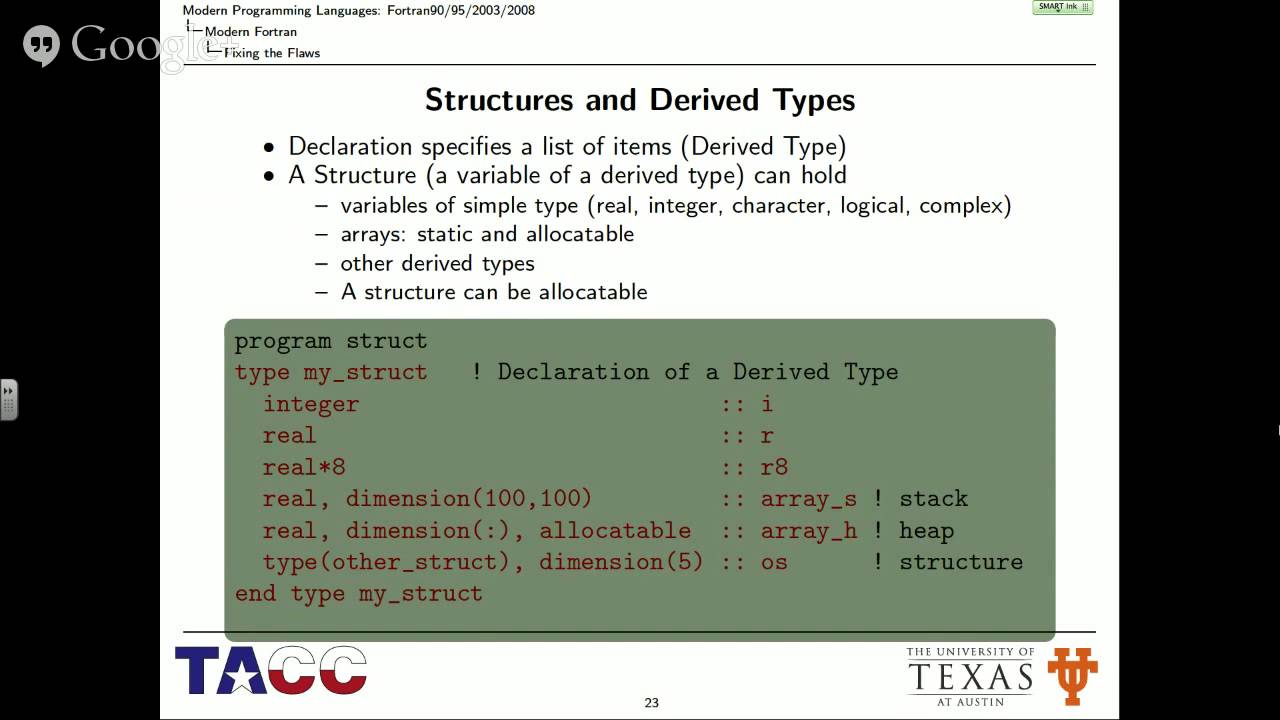



Undergraduate Research Experience Day 3 Morning Fortran 90 95 Programming Youtube




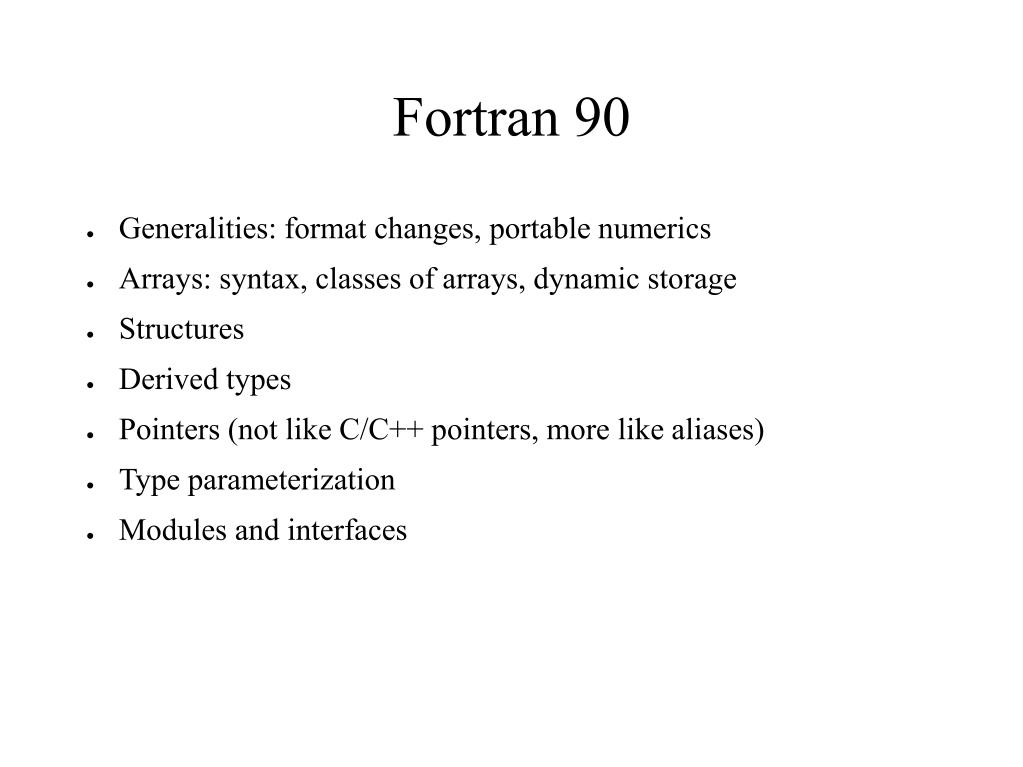
Fortran 90 95 And Fortran 90 Generalities Format Changes Portable Numerics Arrays Syntax Classes Of Arrays Dynamic Storage Structures Ppt Download




Modernizing Modularizing Fortran Codes With 03 Standards




Getting Real With Fortran Qmul Its Research Blog



Fortran Formula Tranlastion




Iso Iec Tr 01 Information Technology Programming Languages Fortran Enhanced Data Type Facilities Iso Iec Jtc 1 Sc 22 Wg 5 Amazon Com Books




Fortran 90 Arrays



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿